PMA光解仪用于生物膜存活率检测
PMA光解仪用于生物膜存活率检测
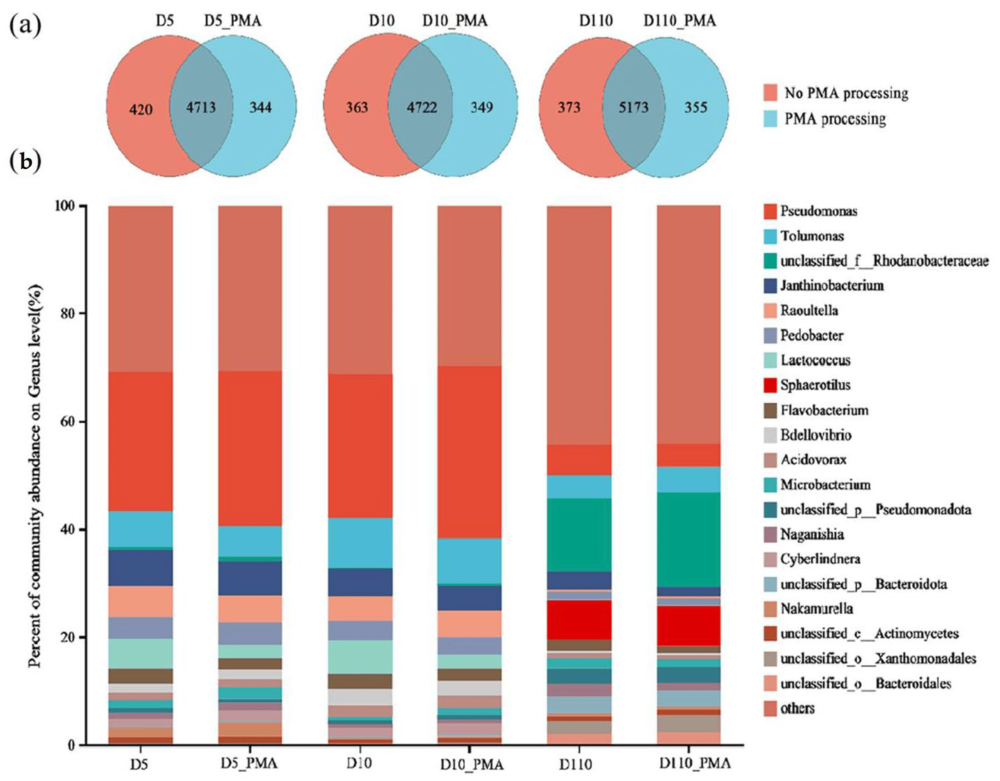
农业农村部农业环境保护研究所发表文献《Revealing the Viable Microbial Community of Biofilm in a Sewage Treatment System Using Propidium Monoazide Combined with Real-Time PCR and Metagenomics》,文献中的实验使用了我公司生产的LUYOR-3419PMA光解仪,,使用单叠氮丙啶(PMA)结合实时定量聚合酶链式反应(qPCR)和宏基因组技术,评估污水处理系统中生物膜的存活率以及存活群落的组成和功能。
文献摘要:
PMA Condition Optimization
We took 500 μL of viable E. coli suspension and dead E. coli suspension (the concentration was 1 × 108 CFU/mL [47]) and put them into 1.5mL transparent PVC centrifuge tubes, respectively, and then added 500 μL biofilm suspension. The mixtures were thoroughly vortexed. Different volumes of PMA solution (Upland Co., LTD.) were added to achieve final PMA concentrations of 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 μM. After thorough mixing, the samples were incubated in the dark at room temperature for 5 min and then exposed to light for 10 min using the LUYOR-3419 LED photoreactor (LUYOR INSTRUMENT CO, LTD). The samples were mixed once for 5 min. The LUYOR-3419 LED photoreactor provided uniform and maximal illumination to 24 × 1.5−2 mL vials, using illumination long-lasting LED lights with 465–475 nm emission from both sides and the bottom to all vials for efficient activation of PMA. The distance between the three light sources and vials was 5 mm, with a strength of 7900 μw/cm2 for each vacancy. Subsequently, they were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 2 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was discarded while the sediment was retained for DNA extraction and qPCR detection. Three repetitions were performed in each condition.
文献地址: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081508
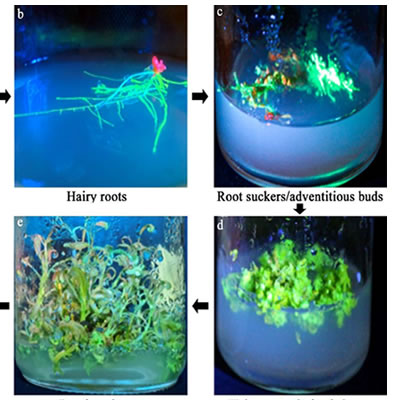 路阳激发光源用于杨树基因的研究
路阳激发光源用于杨树基因的研究
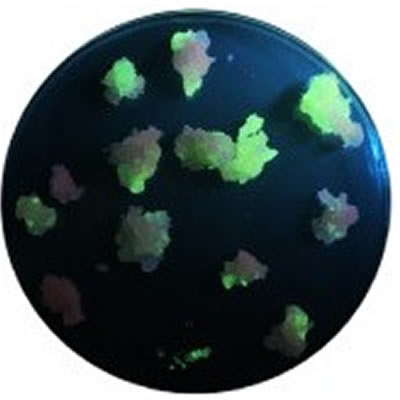 激发光源用于花青素的生物合成的研究
激发光源用于花青素的生物合成的研究
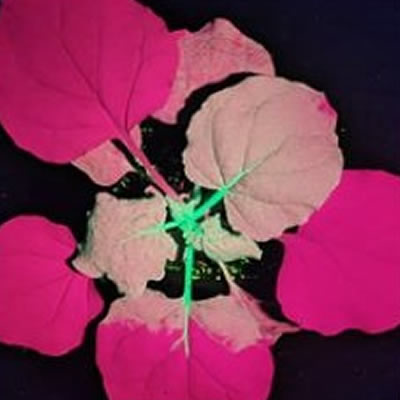 高强度紫外线灯用于观察GFP在植物叶片上的表达
高强度紫外线灯用于观察GFP在植物叶片上的表达
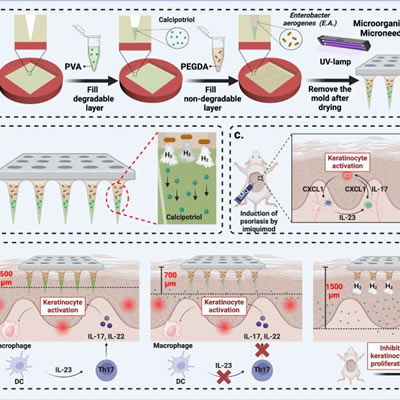 台式紫外灯用于微针制备的固化
台式紫外灯用于微针制备的固化

